Progress in supporting partner countries to reduce the number of children stunted
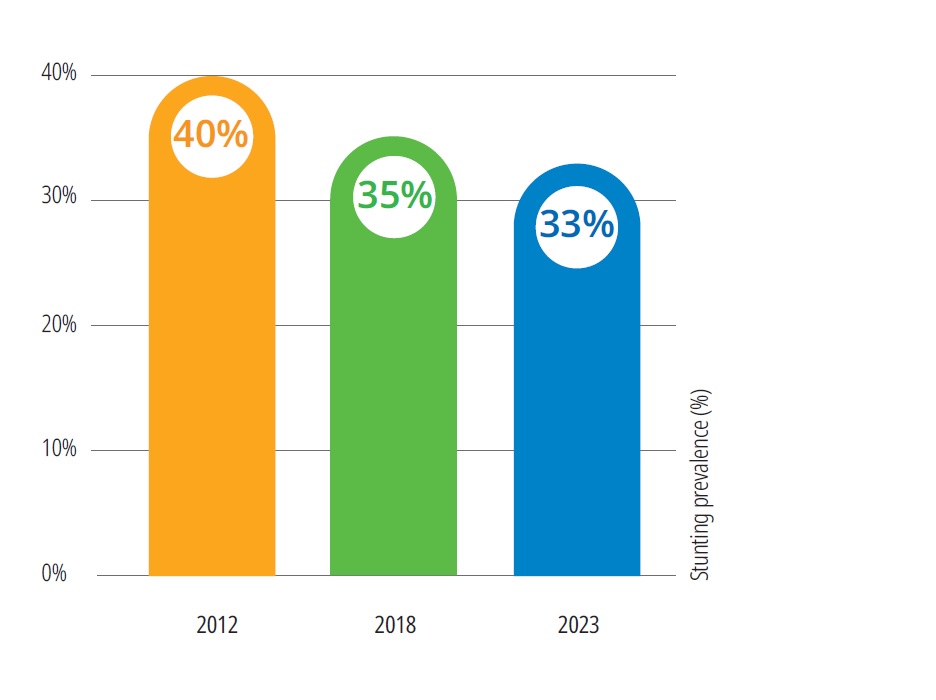
According to current projections this target is ‘on track’ in the 40 baseline countries. Of these countries, 39 have since 2012 reduced the prevalence of stunting, with an average reduction of 7.2 percentage points, or 7.1 million children, as shown in the figure below.
At the global level the prevalence of stunting has been declining steadily, albeit slowly, over the last decade. It is estimated that there are 148.1 million stunted children in the world (22.3% of all children ) in 2022[1]. For comparison the number was 195.5 in 2000.
However, achieving all global World Health Assembly nutrition targets on maternal, infant and young child nutrition will require extension to the SDG timeline (2030) and mobilisation of additional efforts by all countries.
The EU uses the the Stunting Reduction Calculation Tool (SRCT) methodology which sets the trend and projection of child stunting (both prevalence and numbers) in each country since 1990.
[1] UNICEF, WHO, World Bank Group (2023). ‘Levels and trends in child malnutrition. Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates 2023’. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/368038/9789240073791-eng.pd…